林大欽醫師,海芙刀,不孕症治療,精卵捐贈,人工生殖治療,人工受精IUI,試管嬰兒IVF
Artificial Reproductive Technology (ART)
Overview of Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
In civilized countries, such as the United States, Japan, and Taiwan, the child birth of advanced women aged 35 to 39 continues to increase, and even more advanced women over forty years old also increase their possibility of child birth due to infertility treatments.
Due to the advanced age, the egg quality of the elder women becomes worse, and the rate of chromosomal abnormalities becomes higher; therefore, they are prone to have chromosome-abnormal babies and subsequent abortion.
However, in IVF, Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) is designed to check embryo’s chromosomal abnormalities (including abnormal the number of chromosomes and their fragmental deletion, etc.). Proper selection of produced embryos is expected to increase the chance of IVF success.
This technology in IVF is indicated in
1) advanced age, 2) habitual abortion, 3) several IVF failure. Therefore, In popular saying, IVF with PGT is called “ the 3rd generation IVF.
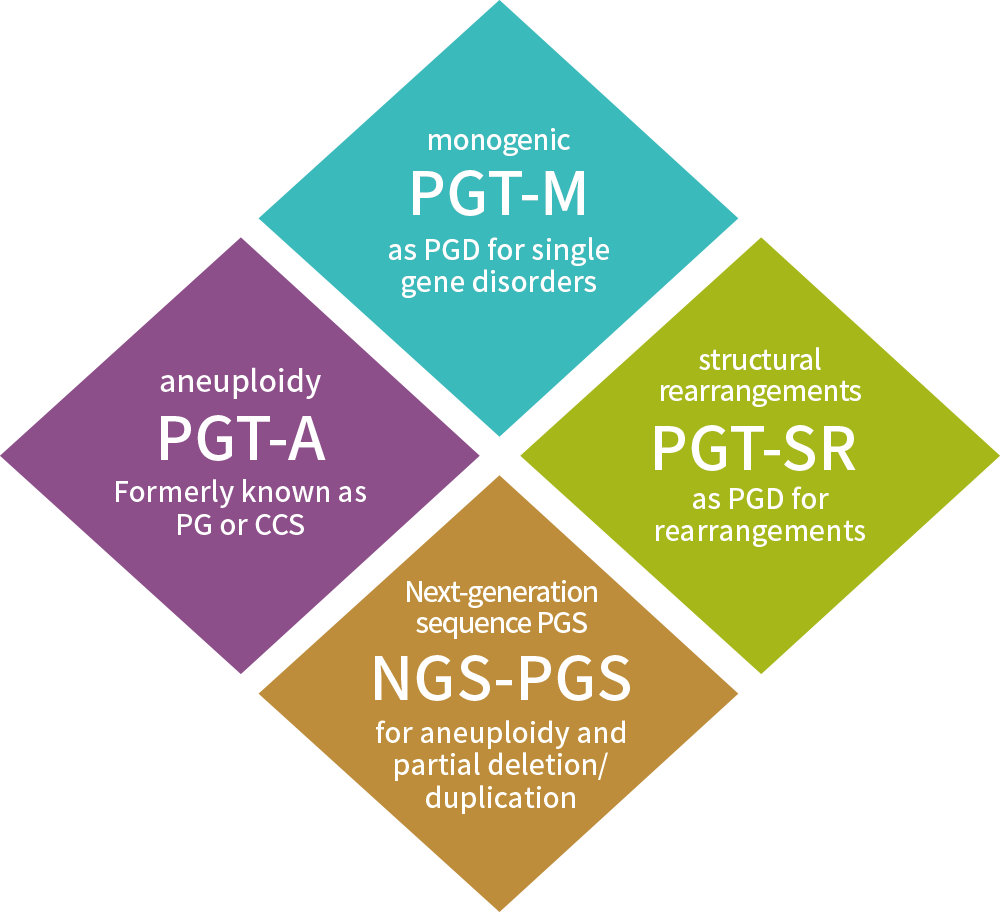
Terminology of Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) is a genetic test performed on embryos produced through IVF。
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidies (PGT-A)
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic/Single Gene Defects(PGT-M)
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Chromosomal Structural Rearrangements (PGT-SR)
There are several old terms for genetic screening in IVF
All of these old terms, PGS, PGD, and CCS etc., are gradually replaced with PGT-A,-M,-SR.
- preimplantation genetic screening (PGS): similar to PGT-A
- preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD): similar to PGT-M
- comprehensive chromosome screening (CCS)
Purpose of preimplantation genetic testing (PGT)
- The purpose of PGT-A is to increase pregnancy rate, reduce miscarriage rate, and prevent aneuploidy diseases (such as Down's syndrome) in IVF.
- The purpose of PGT-M is to block monogenic disease in IVF.
- The purpose of PGT-SR is to block the inheritance of chromosome structure rearrangement in IVF
What is PGT-A? Who need PGT-A?
- A is for aneuploidy:
- PGT-A (preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies): PGT-A is used to test embryos by counting the 46 chromosomes to detect extra or missing chromosomes (“aneuploidy”).
-
Who need PGT-A?
A. Advanced age: Woman in her late thirties and beyond should consider this option.
B. Habitual abortion.
C. Repeated unsuccessful IVF. - The screened embryos have correct number of chromosomes and are the most likely to implant and result a successful pregnancy. It also reduces the chance of having a child with extra or missing chromosomes, such as Down syndrome.
-
How can we detect aneuploidy?
A skilled embryologist removes one or more cells from each embryo. The cells are sent to a laboratory to examine the number of chromosomes in the embryo using an embryo screening method known as “Next Generation Sequencing” (NGS).
What is PGT-M? Who need PGT-M?
- M is for monogenic gene disorders:
- PGT-M (preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disease): PGT-M is used to describe old term of single-gene PGD.
-
Who need PGT-M?
Those who or whose spouse have a known inherited disorder caused by mutations in a single gene. - PGT-M is used to help individuals or couples reduce their risk to have a child with a known inherited disorder caused by mutations in a single gene (“monogenic”), such as cystic fibrosis or Huntington’s disease.
What is NGS? Who need NGS-PGS?
NGS: Next-generation sequencing technology, referred to as NGS, also known as high-throughput sequencing technology, can sequence hundreds of thousands to millions of DNA molecules at a time to read and mark of long and short DNA molecules. It belongs to the second generation of gene sequencing technology, which is often used in infertility reproductive medicine and cancer medicine in medicine.
The most important feature of NGS in reproductive medicine is high-throughput sequencing, which can detect a variety of genetic changes including point mutations, gene copy number changes, and gene recombination (chromosome translocation). It is a tool for PGS and PGD.
Use NGS(next Generation Sequencing) to screen out embryos with normal chromosomes. The NGS-PGS in our institute is performed with Illumina NGS equipment and MiSeq testing platform. The provider has Illumina CSPro certified testing quality. NGS-based PGS adopts large-scale high-throughput sequencing and high-sensitivity detection, which can screen out genetic variants that cannot be read by previous technologies, and can effectively improve embryo implantation and pregnancy rates.
According to literature, the results of using NGS-based PGS are consistent with the results of using fluorescent chip (aCGH) screening. NGS-based PGS has a high detection rate of 99.98% for aneuploidies that easily cause pregnancy failure.
- Infertile couples may require artificial reproduction technology
- Habitual abortion
- IVF failure more than 3 times (may be affected by aneuploidy)
- Advanced maternal age
- Inherited chromosomal abnormalities (e.g. balanced translocation)